When choosing the best flooring for your latest project, not only can the choices often seem overwhelming, but so can the terms used. So, we’ve created a glossary of terms used with flooring projects to help make it easier to understand the differences between the wide range of flooring products available.
A B C D E F G H I J K LM N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A
Above Grade – a suspended floor above ground level with a minimum of 18 inches of ventilated air space below. Most commonly used over a basement.
Acclimation – also referred to as acclimatisation, is the time flooring (particularly wooden flooring) takes to adjust in regards to moisture and humidity – flooring must be left to acclimatise before installation.
B
Backing – fabrics that form the back of the carpet to provide reinforcement and stability.
Below-Grade – flooring that is partially or completely below the ground level nearby, and in direct contact with the ground.
Blend – a carpet made up of 2 or more different types of yarns or fibres.
Blind Nailing – when nails are set into flooring boards in tongue and groove installations at 45 degrees.
C
Carpet Cushion – a layer of padding between the carpet and floor to add softness beneath your feet and protect against wear and tear.
Cross Ply Construction – engineered hardwood that is more durable and stable due to being constructed by planks that are stacked in alternating directions. These alternating planks mean the boards are not affected as much by moisture or humidity.
Crowning – when wooden boards warp, and the centre of the board is higher than the sides.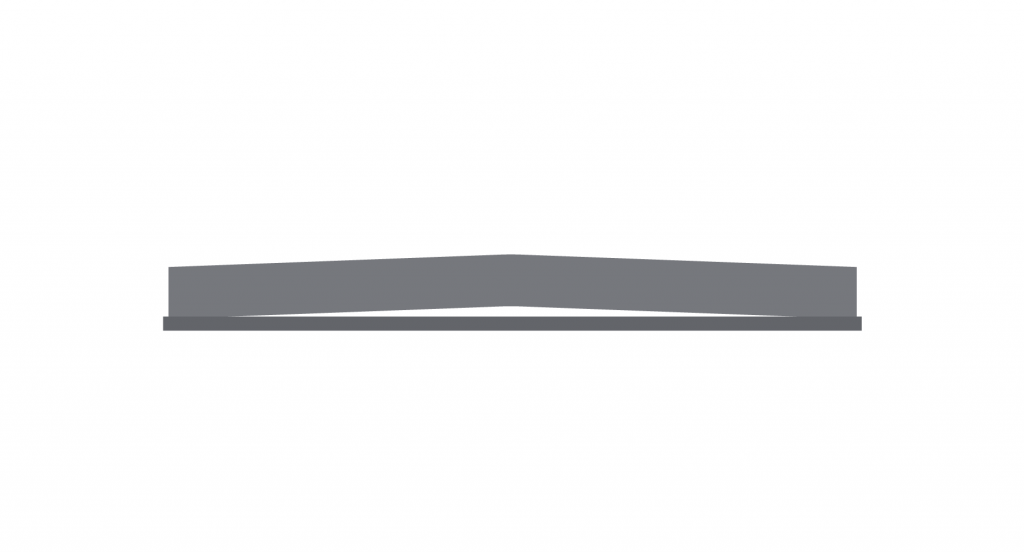
Cut Pile Carpets – cut pile carpets consist of loops of yarn that are then cut to form a more regular appearance than loop pile carpets. Cut pile carpets are the most popular type of carpet and can come in a range of different lengths and thicknesses.
Cut and Loop Carpets – these carpets are a combination of cut pile and loop pile carpets, where the taller loops are cut whilst the smaller loops are not, which creates a sculpted pattern and texture.
D
Denier – the thickness of each strand of carpet. Generally, the thicker the better, but the thinner denier results in a softer feel.
E
Engineered Wood – hardwood boards constructed from multiple layers of wood, as opposed to solid wood boards which are constructed from a single piece of wood.
Expansion Gap – the area around the perimeter of a floor that has been left free to allow for expansion.
F
Feature Strip – a strip of wood or material that is used at a threshold, as a border or to create a point of interest.
Floating Floor – a floor that is not fixed to the subfloor using nails or other fixing methods, but instead consists of flooring planks being fixed to each other. This is often a chosen method of flooring due to the speed at which it can be laid.
H
Herringbone – a laying design consisting of boards or tiles laid in a staggered V, or chevron pattern, most commonly used with small rectangular tiles. The style has a resemblance to the bones of a herring fish, which is where the name is derived from.
L
Lacquered Finish – a resin that is normally clear, to form a thin film over the flooring, giving a glossy finish which is easy to maintain.
Laminate Flooring – constructed by pressing an image of wood, tiles or other design onto high-density fibreboard, with a clear coat resin for durability. Easy to install, laminate flooring has a click-locking system.
Loop Pile – loop pile carpets are made from uncut loops of yarn, to give a rugged and rough appearance, that can be in a range of textures.
Linoleum – one of the first forms of resilient flooring, linoleum is made from linseed oil, wood dust, cork, resin, and other materials.
M
Modular Carpet – also known as carpet tiles, that are typically 18” x 18” but may vary.
Moisture Content – the amount of moisture in wood, which is generally expressed as a percentage of the weight of the wood.
Moulding – trims, and other transition pieces of wood or tile that are used to complete the project.
P
Parquet – a style of flooring that consists of a number of tiles or wooden boards arranged in a geometric pattern.
Prefinished Flooring – flooring which has been treated and is ready for installation.
R
Random Length – random length packs of boards contain a range of different lengths between specified shortest and longest lengths.

Reclaimed – wood or tiles that have already been used in an old building or another application, and have been removed, refurnished and repaired if needed, ready to be used for a new project.
S
Shedding – A newly installed carpet will naturally shed for the first few days, and will require vacuuming for the first few days to remove loose fibres.
Stitch Rate – how close yarns are on a carpet, the stitch rate varies depending on the speed at which the carpet moves through the machinery. The lower the tufts per inch, the poorer quality.
Solid Wood – wooden boards that have been constructed from a single piece of wood, as opposed to engineered wood which is made up of several layers of wood.
Subfloor – the layer of the floor that provides structural support. The flooring can be directly applied to the subfloor, or onto an underlayment if the subfloor is challenging to install flooring onto.
T
Threshold – where one flooring level transitions to another flooring type, a finishing piece is applied.
Tongue and Groove – when tiles, flooring or floorboards fit together easily edge to edge – one side has a tongue whilst the other has a groove, and the tongue fits precisely within the groove to create a strong flat surface that locks together.
U
Underlayment – material that is laid above the subfloor before the main flooring is laid, to create a suitable installation surface. 
V
Veneer – a layer of solid wood that is glued to a core, creating engineered hardwood flooring.
W
Wire Brushing – a wire brush is used to create a distressed appearance to wooden flooring.















